Essential Climate Variable (ECV)
An Essential Climate Variable (ECV) is a physical, chemical or biological variable or a group of linked variables that critically contributes to the characterization of Earth’ s climate. ECV datasets provide the empirical evidence needed to understand and predict the evolution of climate, to guide mitigation and adaptation measures, to assess risks and enable attribution of climate events to underlying causes and to underpin climate services. They support the work of United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
GCOS
The Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) works towards a world where climate observations are accurate, sustained and access to climate data is free and open. It regularly assesses the status of global climate observations and produces guidance for its improvement. It is co-sponsored by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the Inter-governmental Oceanographic Commission of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (IOC-UNESCO), the United Nations Environment Program (UN Environment) and the International Science Council (ISC). GCOS expert panels maintain definitions of Essential Climate Variables (ECVs) which are required to systematically observe Earth`s changing climate.
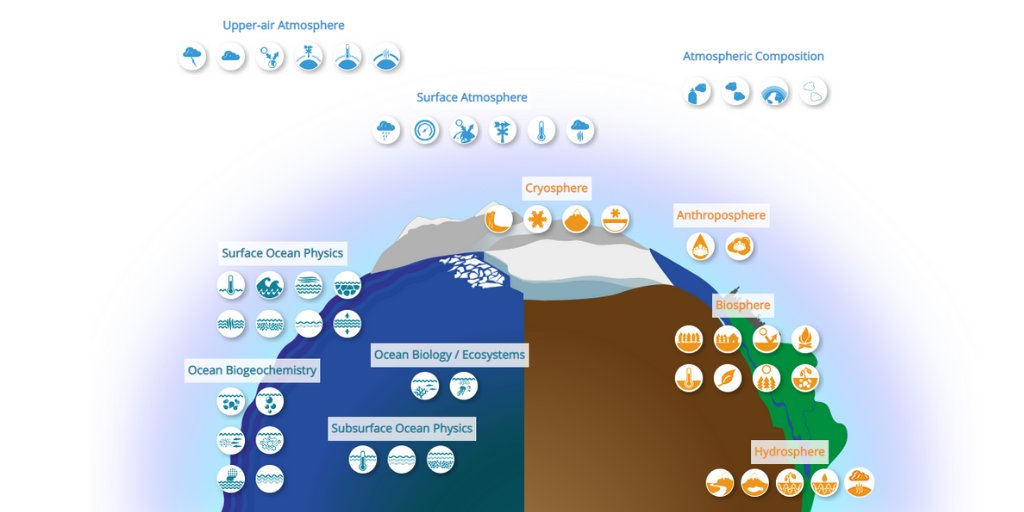
GCOS currently specifies 54 ECVs under different categories & sub-categories as shown below. The expert panels regularly develop plans on how to sustain, coordinate and improve physical, chemical and biological observations. They identify gaps by comparing the existing climate observation system with these ECVs.
Atmosphere |
Surface |
|
Upper-air |
|
Atmospheric Composition |
|
Land |
Hydrosphere |
|
Cryosphere |
|
Biosphere |
|
Anthroposphere |
|
Ocean |
Physical |
|
Biogeochemical |
|
Biological/ecosystems |
|